
Types of reliability and how to measure them. Key Takeaways: What is Validity Validity is the measure of whether or not your test is accurate. While these criteria are related, the terms aren’t interchangeable. Ideally, you want your equipment to be both reliable and valid or consistent and accurate be it a thermometer, questionnaire, or scale. In the fields of science and technology, the terms reliability and validity are used to describe the robustness of qualitative and quantitative research methods. Steps are taken to make sure the work’s findings are the result of experiences and ideas of the informants, and that evaluation findings are arrived at by considering solid evidence. Validity is all about accuracy in your measurements, while reliability determines consistency. The processes within the study are reported in detail, so that a future researcher can repeat the work Is it important to consider the findings of the study within the broader context of other people and settings, and whether similar projects and methods conducted in different environments would be of value. Reliability in qualitative research: Credible The same test conducted by different people.ĭifferent versions of a test which are designed to be equivalent.
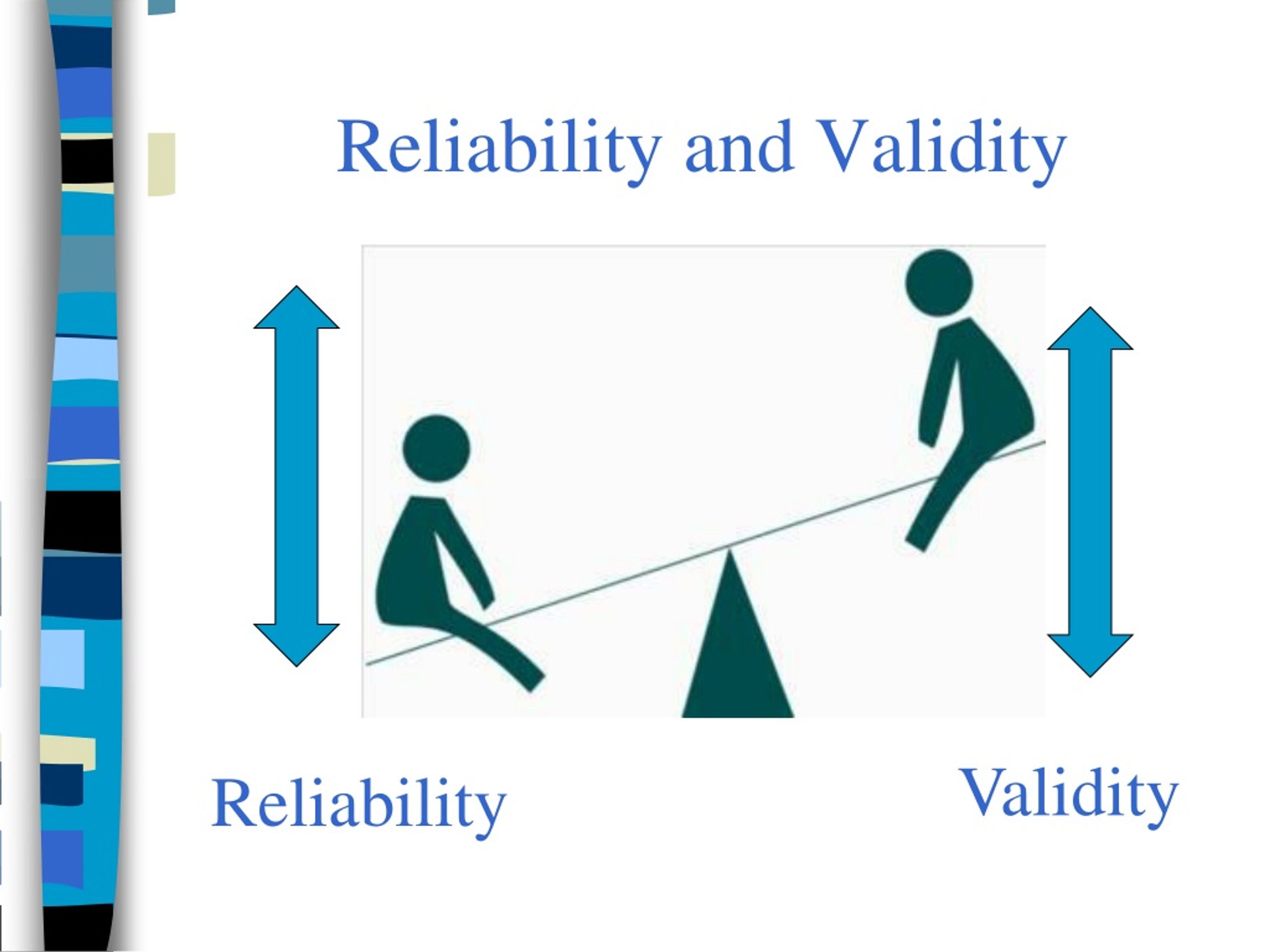

Reliability in quantitative research: Test-retest Reliability and Validity EXPLORING RELIABILITY IN ACADEMIC ASSESSMENT Written by Colin Phelan and Julie Wren, Graduate Assistants, UNI Office of Academic Assessment (2005-06) Reliabilityis the degree to which an assessment tool produces stable and consistent results. the measurement could apply to others/the same result would happen each time.the extent to which a research instrument consistently has the same results if it is used in the same situation on repeated occasions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
